Bladeflex Postural Benefits
Good posture is a combination of balanced strength and flexibility in the skeletal muscles, enabling people to walk, sit or stand in a graceful manner. Conscious activation of the postural muscles is important, especially when sitting or standing for long periods of time. There are 3 key areas of the body that Bladeflex will help you with when correcting your posture.
The Neck
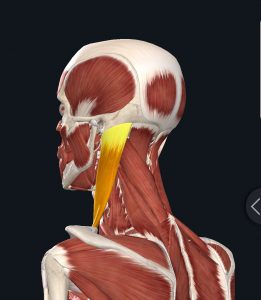
Weighing between 10-12 pounds, the average adult head must be carried over the spine in balance to avoid pain and discomfort in the neck and spine. There are 26 muscles in the neck, including the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius, which are responsible for the gross motor movement in the muscular system of the head and neck. They move the head in every direction, pulling the skull and jaw towards the shoulders, spine, and scapula. Poor posture can cause neck pain by straining those muscles and ligaments, resulting in injury over time.
The Back
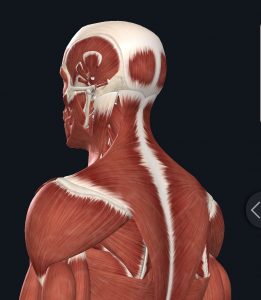 Anchoring the shoulder blades to the spine is a flat, triangular shaped muscle called the trapezius. This muscle covers the neck, shoulders and thorax. Effective posture necessitates that the trapezius muscle is strengthened equally in the front and back of the body. The most common imbalance of this muscle is overextended across the back, and too short or tight across the chest, enabling the shoulder blades to pop out like wings, which often causes pain and discomfort. Proper scapular mobility is an important part of a healthy back.
Anchoring the shoulder blades to the spine is a flat, triangular shaped muscle called the trapezius. This muscle covers the neck, shoulders and thorax. Effective posture necessitates that the trapezius muscle is strengthened equally in the front and back of the body. The most common imbalance of this muscle is overextended across the back, and too short or tight across the chest, enabling the shoulder blades to pop out like wings, which often causes pain and discomfort. Proper scapular mobility is an important part of a healthy back.
The Shoulders
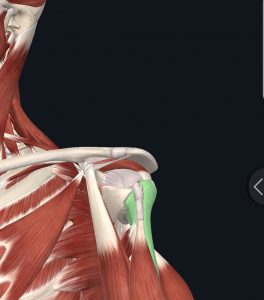 Shoulder pain is very common problem that can affect your ability to do everyday tasks. In particular, subacromial impingement is a frequent cause of shoulder pain. Subacromial impingement occurs when there is reduced space between the head of the humerus and the acromion process. As a result of the reduced space between the head of the humerus and the acromion process, tissues in that area get compressed. Strengthening the muscles that stabilize the scapula and support maintaining the subacromial space is necessary for reducing the compression of tissues and reducing shoulder pain. The trapezius and serratus anterior are key muscles for maintaining stability of the scapula.
Shoulder pain is very common problem that can affect your ability to do everyday tasks. In particular, subacromial impingement is a frequent cause of shoulder pain. Subacromial impingement occurs when there is reduced space between the head of the humerus and the acromion process. As a result of the reduced space between the head of the humerus and the acromion process, tissues in that area get compressed. Strengthening the muscles that stabilize the scapula and support maintaining the subacromial space is necessary for reducing the compression of tissues and reducing shoulder pain. The trapezius and serratus anterior are key muscles for maintaining stability of the scapula.